Ovulation Induction
Hope Healing Happiness
in Fertility Care
Ovulation Induction (OI) is a fertility treatment that helps women release eggs from their ovaries using medicines.

Ovulation Induction
What is Ovulation Induction ?
Ovulation Induction (OI) is a fertility treatment that helps women release eggs from their ovaries using medicines.
- Normally, a woman releases one egg per month.
- Some women don’t release eggs regularly, or at all.
- OI medicines help regulate or stimulate ovulation so that the chances of pregnancy increase.
- It is often done together with timed intercourse or intrauterine insemination (IUI).

Who Needs Ovulation Induction ?
OI is useful for:
- Women who don’t ovulate regularly, such as those with PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome).
- Women who have irregular or very long cycles.
- Couples with unexplained infertility (everything looks normal but pregnancy is not happening).
- Women using donor sperm.
OI is not usually recommended for:
- Women over 38 years old (IVF often works better).
- Women with blocked or severely damaged tubes.
- Women with severe endometriosis.
- Couples with very low sperm count or poor sperm quality.
Types of Ovulation Induction Medicines
Tablets (Oral medicines) – usually the first choice
- Clomiphene citrate (Clomid/Serophene): Helps the body produce more hormones that trigger ovulation. Works in many women but can thin the womb lining if used for too long.
- Letrozole (Femara): Often used in PCOS patients. It has fewer side effects and is now the preferred option in many clinics.
Injections (Gonadotropins like FSH or hMG) – used if tablets don’t work
- Directly stimulate the ovaries to grow eggs.
- More effective but carry higher risks (twins, triplets, ovarian overstimulation).
Other supporting medicines
- Metformin (in women with PCOS and insulin resistance).
- hCG injection (“trigger shot”) given when the egg is ready, to cause ovulation.
Step Process
How Does the Procedure Work ?
Step 1 : Initial check-up
- Blood tests to check hormone levels.
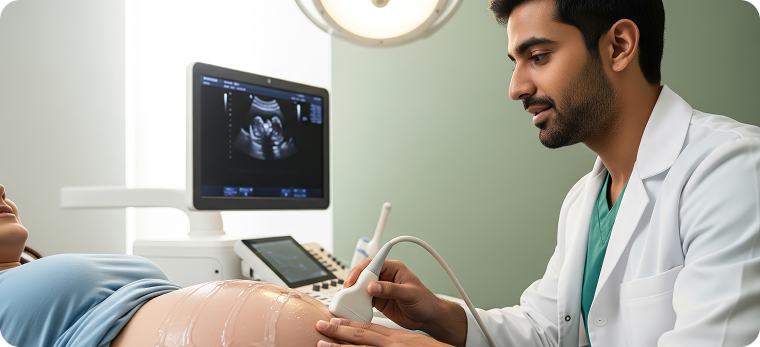
- Ultrasound scan of the ovaries and uterus.
- Partner’s semen test.
- Tubes checked for blockage (HSG/SHG).
Step 2 : Stimulation phase
- Medicines (tablets or injections) are started early in the menstrual cycle (Day 2–5).
- These encourage the ovaries to grow 1–3 eggs.
Step 3 : Monitoring phase
- Ultrasound scans are done every few days to see how the eggs are growing.
- Sometimes blood tests are done to check hormone levels.
Step 4 : Triggering ovulation
- When the egg is mature, a hCG injection is given.
- Ovulation happens about 36–40 hours later.
Step 5 : Conception attempt
- The couple is advised on the best time for intercourse.
- Or, the doctor may perform an IUI (placing sperm directly into the uterus).
Results of Ovulation Induction
Tablets (Clomiphene/Letrozole):
- 70–80% of women will ovulate.
- 20–25% will get pregnant in each cycle.
Injections (Gonadotropins):
- Higher pregnancy rates (up to 30–40% per cycle with IUI).
- But also higher risk of twins or triplets.
Possible risks:
- Multiple pregnancy (twins, triplets).
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) – ovaries become swollen and painful (more common with injections).
- May not work in women with poor ovarian reserve or blocked tubes.